Open source contribution policies that don’t suck!
Tobie Langel, Principal, UnlockOpen tobie@unlockopen.com
A presentation at OpenChain Webinar in May 2020 in by Tobie Langel

Tobie Langel, Principal, UnlockOpen tobie@unlockopen.com
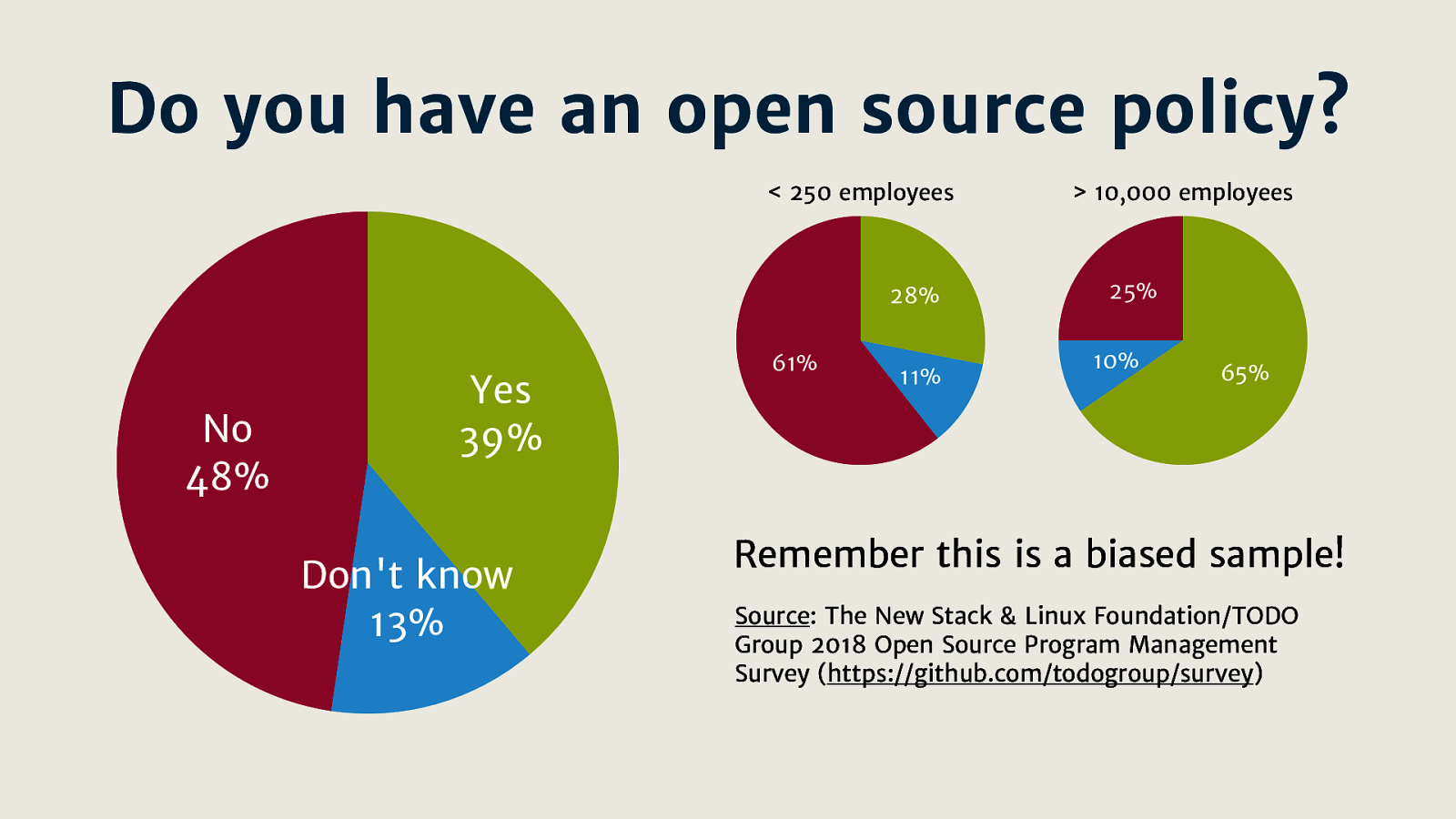
Source: The New Stack & Linux Foundation/TODO Group 2018 Open Source Program Management Survey (https://github.com/todogroup/survey)

Contrary to popular belief, it does not mean that you don’t have an open source policy at all.
It means that you don’t have a written one.
You have a policy, whether it is written down or not. It could range from “no open source at all” to “anything goes.”
—Heather J. Meeker, Open Source Licensing Specialist, author of Open Source for Business.

Think you’re in the right camp because you have an open source contribution policy? Think again!
None of these are fun!
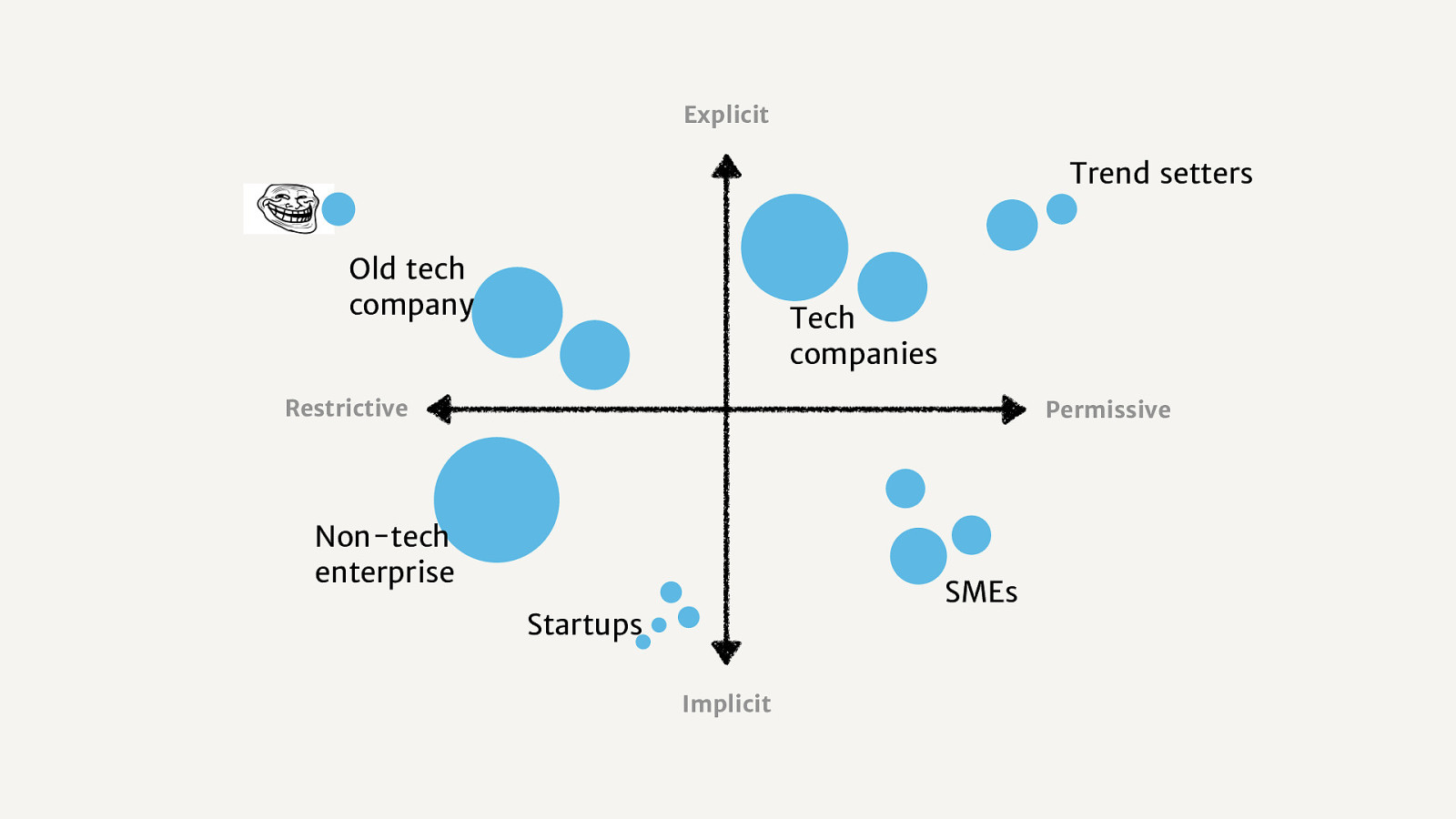

Permissive. Allows open source contribution to be an integral part of the company’s engineering culture and best practices. Based on trust and autonomy.
Explicit. The decision making process is well documented and transparent.
Informative. The policy explains the why an helps educate engineers.
Frictionless. Avoid bureaucracy, red tape, lengthly back and forth with legal, etc.

Minimizes risk. Avoid:
Consistently followed across the company. Keep contribution under your radar. Avoid compliance issues.
Savvy about written information. Sometimes you want a paper-trail (e.g. compliance), sometimes you don’t.
Doesn’t drown critical problems in a sea of menial issues.

Engineering to be happy and productive.
Risks minimized and well understood.
Good communication between legal and engineering.
Alignment with Business goals.
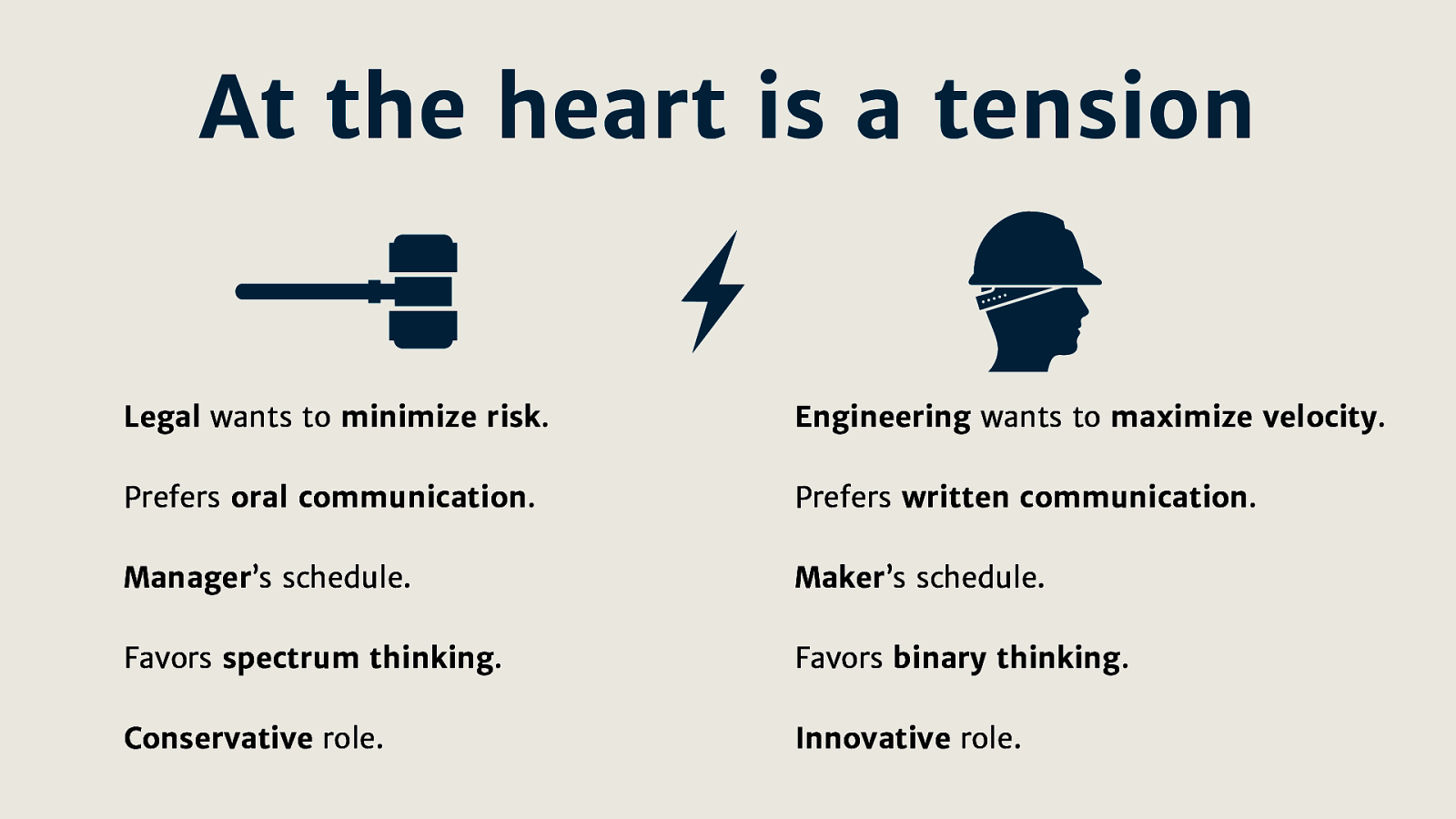
Legal wants to minimize risk. Engineering wants to maximize velocity.
Prefers oral communication vs. prefers written communication.
Manager’s schedule vs. maker’s schedule.
Favors spectrum thinking vs. favors binary thinking.
Conservative role vs. innovative role.

Acknowledge that this tension is normal. It’s just checks and balances.
Listen to both sides.
Remind them that their role is to help achieve common business goals.
Find common ground. A good policy will improve the life of both sides.
Align your open source activity with your business goals. If you are a patent troll, then don’t do open source.
Accept that your open source policy will change with your business.

The realm of OpenChain

Well understood problem, essentially:
Tip: a common issue is missing licenses. Equip engineering with a process (and issue or pull request templates) to request proper OSI-approved licenses.

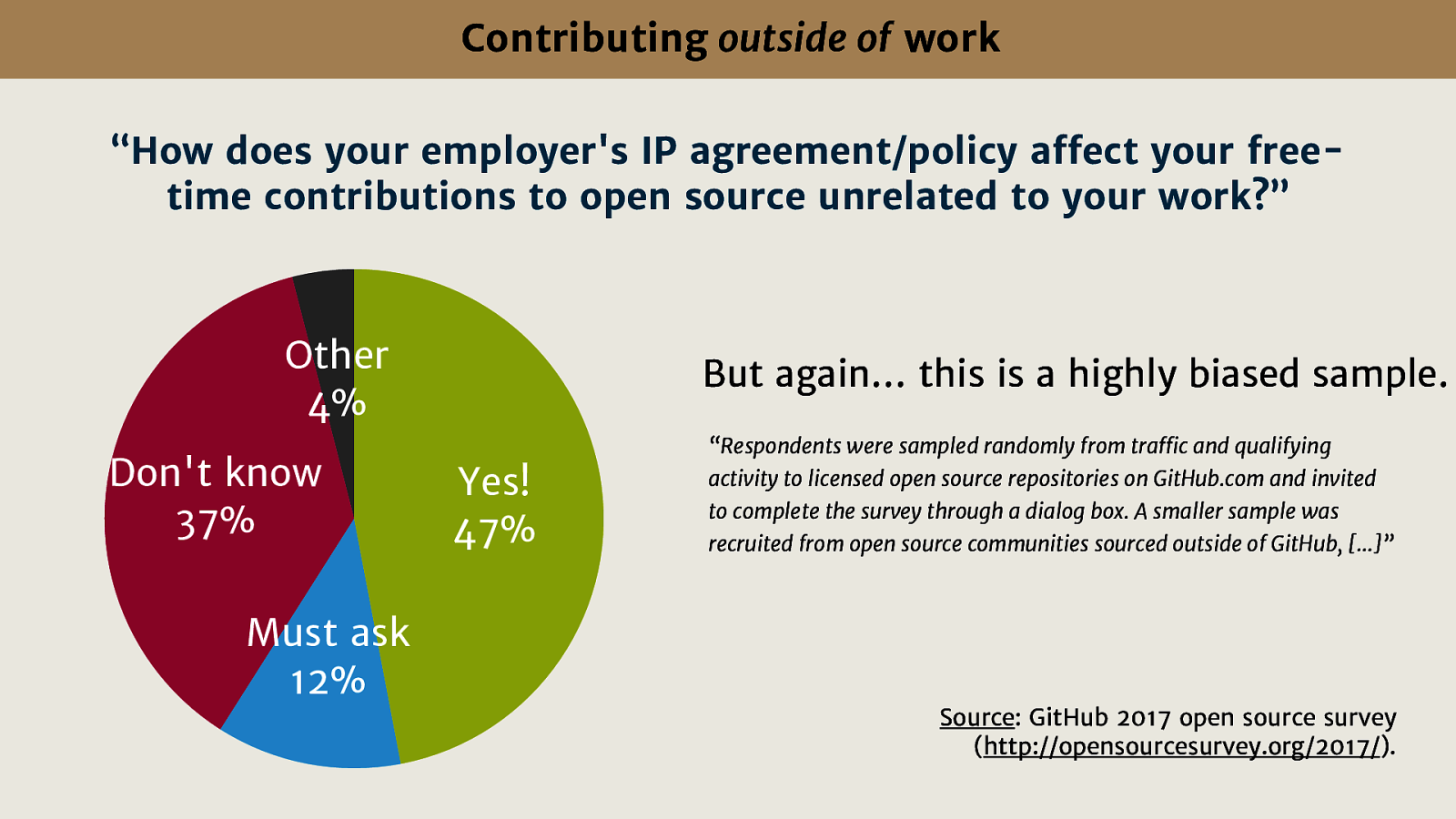
“Respondents were sampled randomly from traffic and qualifying activity to licensed open source repositories on GitHub.com and invited to complete the survey through a dialog box. A smaller sample was recruited from open source communities sourced outside of GitHub, […]”
Source: GitHub 2017 open source survey (http://opensourcesurvey.org/2017/).







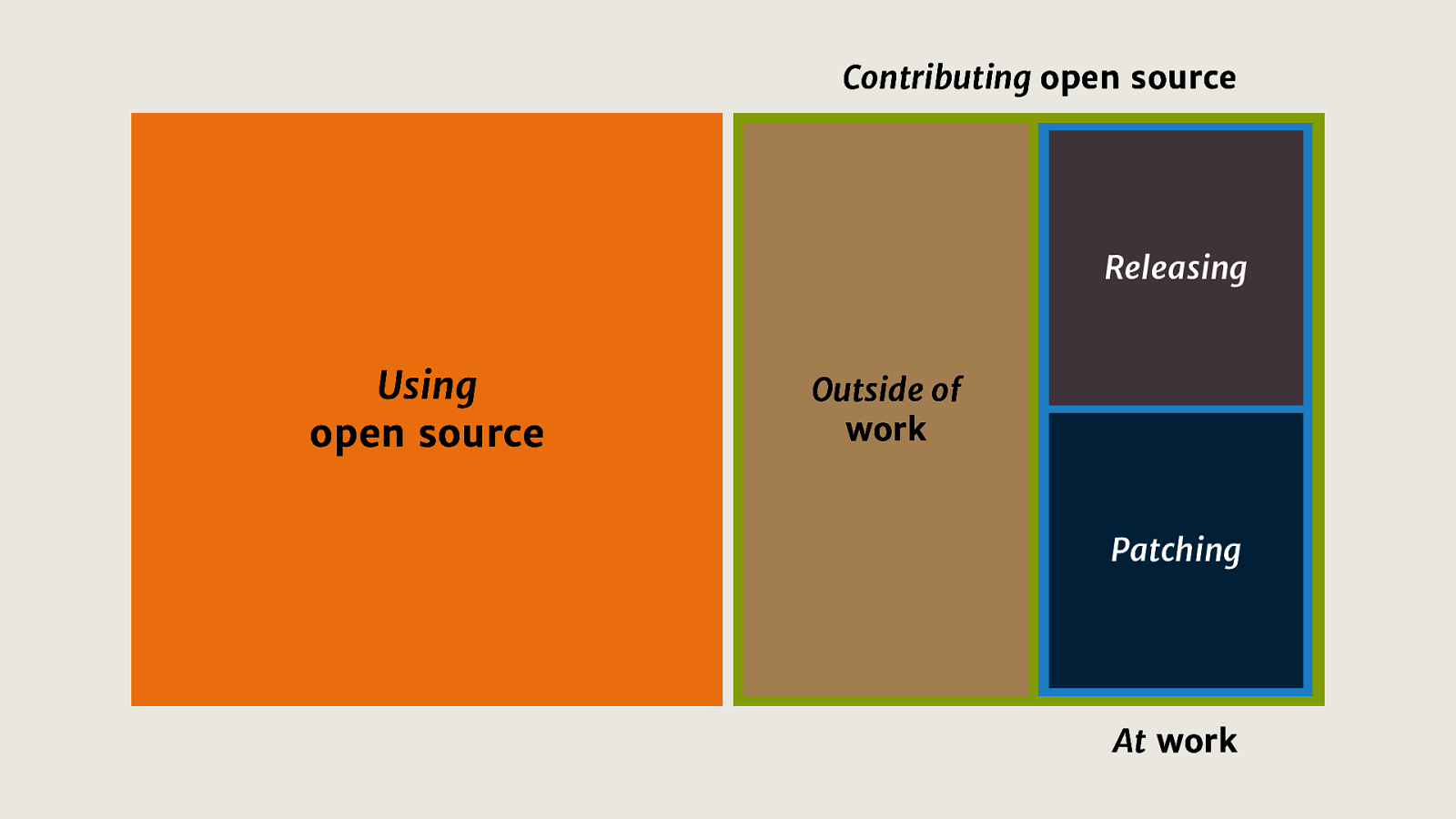


Using such a system, Adobe was able to shorten it’s review time from 4.6 days to 4.6 hours.
But there’s more. The data collected can help:

Tobie Langel (@tobie) Principal, UnlockOpen tobie@unlockopen.com